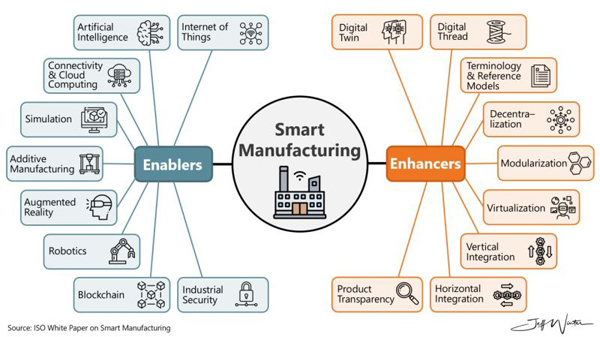
Smart Manufacturing
According to ISO – International Organization for Standardization, we are at a stage within Industry4.0 where some of the new disruptive technologies are mature enough to be leveraged by the industry (referred to as “Enablers“) . As part of this journey, there are also a set of design principles that are currently under development and of high relevance for archiving successful implementation of smart manufacturing (referred to as “Enhancers”)
Three Key characteristics that allowed technologies to become “Enablers” :
- Cheap and abundant data storage
- Fast and responsive computers and calculation power
- Ubiquitous and place-independent connectivity
Together these Enablers serve as the basis for today’s accelerated digital transformation.
When the “Enablers” are fully utilized along with the “Enhancers” there will bound to be new disruptive scenarios as we collectively transition into a “Smart Industry”. The future effects will lead to:
Circular manufacturing : the possibility to make products and production more sustainable and take advantage of retired products and their collected lifecycle information, filter out the essence, and use feedback for improving the manufacturing processes as well as the product itself.
Model-based product and production : the ability to utilize models at every point in the product lifecycle for the optimum use of the product.
Fully automated factories : the ability to use new technologies to enable new configurations of production automated to a very high degree.
Product personalization : the possibility to make mass-produced products more personalized
Predictive maintenance : the possibility to act prior to an unfavorable event (e.g. failure) and use in-process monitoring to enable the identification of the optimum time to replace parts, and hence maximize the service life.
Edge computing : the possibility to have all automation, including real-time control, in the edge of the cloud.
Servitization : the possibility to augment traditional physical products with related services. Hence, the product becomes a by-product of the service.
Data – driven business models : business models that are developed and customized based on data from the business. The more data, the better the business model.
For more information, I encourage you to read the full white paper here:
https://lnkd.in/epYbS9re
About the Author :

Jeff Winter is an Industry 4.0 & Digital Transformation Enthusiast | Business Strategist | Avid Storyteller | Tech Geek | Public Speaker
Jeff Winter with over 15 years of experience working for different industrial automation product and solution providers, Jeff has a unique ability to simplify and communicate complex concepts to a wide range of audiences, educating and inspiring people from the shop floor up to the executive board room. As part of his experience, Jeff is also very active in the community of Industry 4.0.
Jeff is a part of the International Board of Directors for MESA (Manufacturing Enterprise Solutions Association), he is in the leadership committee for the Smart Manufacturing & IIoT Division of ISA (International Society of Automation), he is a U.S. registered expert for IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) as a member of TC 65, and also part of Purdue University’s Smart Manufacturing Advisory Board.
Mr. Jeff is Accorded with following Honors & Awards :
https://www.linkedin.com/in/je
Mr. Jeff Winter is Bestowed with the following Licenses & Certifications:
https://www.linkedin.com/in/je
Mr. Jeff is Volunteering in the following International Industry Associations & Institutions:
https://www.linkedin.com/in/je
He can be contacted at :
Email : [email protected], [email protected]
LinkedIn : https://www.linkedin.com/in/jeffreyrwinter/
Also read his earlier Articles :