Data protection by design and default to comply with UK GDPR
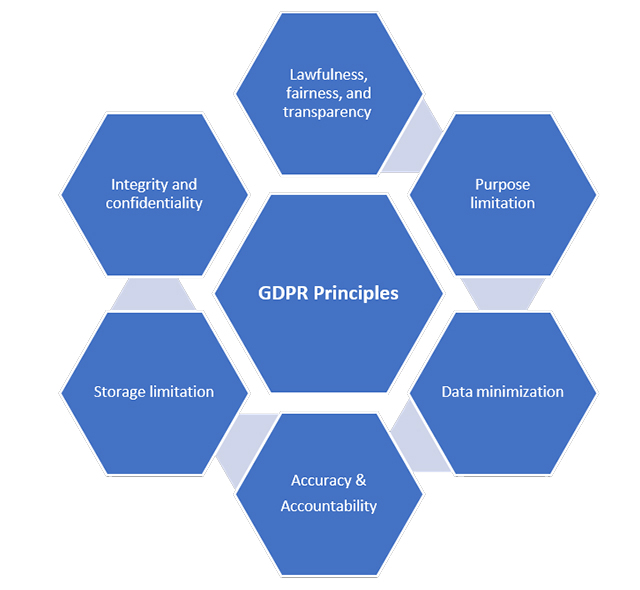
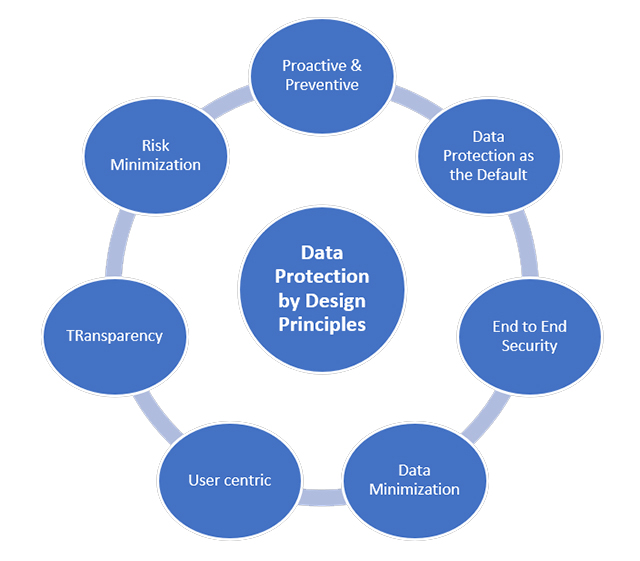
Data protection by design and default is a key element of the UK GDPR’s risk-based approach and its primary focus is on accountability. According to GDPR, data protection by design and default means “an appropriate technical and organizational controls and measures required to implement the data protection principles and safeguard individual rights”. Privacy by design focuses on embedding privacy protection measures throughout the organizational technical infrastructure including the design, development, build and running for software, products, processes and services to ensure personal data processed by these means is managed, secured, and the risk to the data subject is significantly reduced. The GDPR’s key Article 25 indulge controllers to adopt technical and organizational measures that, by design, implement data protection principles into data processing and protect the rights of individuals whose personal data is processed or utilized.
Article 25 of the GDPR—titled “Data Protection by Design and by Default” is the primary source on the need for designing privacy by default and implement control measures to improve privacy posture of the organization. Implement data-protection principles in an effective manner and integrate the necessary safeguards into the processing in order to meet the requirements of the GDPR and protect the rights of data subjects. Privacy by Design and default means that organizations need to consider privacy from the first design stages and throughout the complete development process of any new processes or services that involve processing of personal data. This means that it is no longer just about data protection but rather about designing and building systems so data is inherently protected.
It’s vital to acknowledge that data privacy is critical and ensure this message resonates throughout the organization. It should be integral to the business culture. From the top down, the importance of user privacy must be encouraged, throughout all business practices and ensure that everyone respects this. Ensure that you design and build in the necessary controls to enable consumers to enforce their privacy requirements and the level of protection that they require. Flexibility ensures that users can provide privacy and data protection for varied conditions and environments to support unique and individual security requirements better.
There has always been a strategy that organizations have been following that “Data is always good, everything is important, collect as much as you can and use it when required.” This thinking needs a change while adapting to GDPR’s data minimization requirement, organizations must limit the data collection, define purpose of data requirement and store it in a secured manner of the required data only. Processing of personal data complies with various restrictions to protect the data and avoid data exploitation or losing the data in large numbers.
Exceptions to the GDPR:
Under the GDPR, there are two significant exceptions to note –
The first exception is for companies with less than 250 employees. Organizations in this category are not fully exempt, but they enjoy a more lenient coverage under the regulation. However, such companies must fully comply with the GDPR when:
- Their processing activities may risk the rights and freedoms of data subjects
- They process sensitive personal data or process data frequently, or
- They process a special data category relating to “criminal convictions and offenses”
Secondly, the GDPR does not apply to individuals or companies involved in purely “personal or household activities”. Its scope only covers “commercial or professional activities.”
Procedures for Responding to Privacy Requests:
A major component of GDPR compliance is responding to data subject requests as they come in. There are several types of requests:
- Access requests
- Deletion requests
- Requests to correct inaccuracies
- Object to processing
- Requests to limit processing
- Opt-out of automated decision-making
Responding to any of these data subject requests can be demanding, and they generally must be completed within a one-month time limit. This requires advance planning on the part of controllers, and failure to put procedures in place will not excuse inadequate or late responses.
Simplified GDPR Compliance:
As the principle of data protection by design makes clear, GDPR compliance is not just cosmetic changes, but, stringent in the way it has to be aligned with the regulatory requirements. It requires vigilant planning and thoughtful action. Each and every GDPR principle has its defined process and steps to follow to ensure data security is embedded at the designing stage itself by default.
Article 25 of the GDPR requires a data protection by design and default, data controllers or data processors or sub processors based on the role that as organization is playing, it must ensure that robust planning is done to put technical and organizational controls in place to define the process of processing personal data. Building compliant process means that the new functionality needs to be embedded within the organization structure in a very structured manner to meet both the organizational policy and regulatory standard requirements to deliver privacy protected services.
Key takeaways to ensure GDPR compliance:
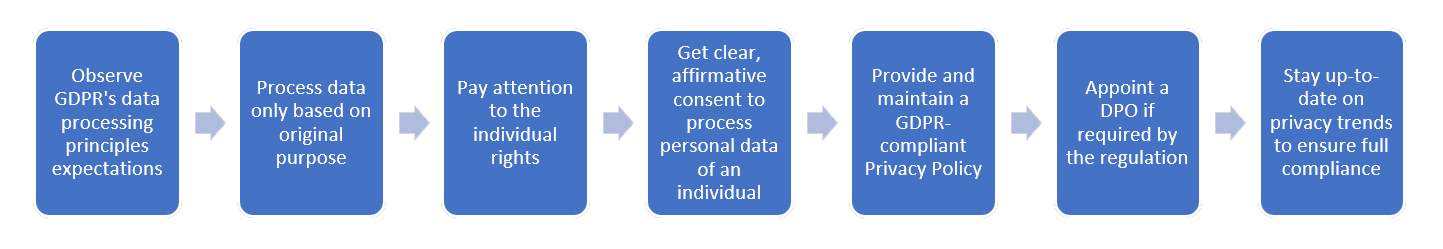
Data Privacy policies should be implemented at a technical and business process level. When personal data is no longer required, it needs to be destroyed or anonymized. Consent management for approving, anonymizing the data, storage of data and other data treatments is an integral part of near-future systems to ensure controlled processes are defined to avoid unauthorized access or data leakage.
Best Practices to safeguard Personal Data:
- Try to prevent crises rather than seeking solutions
- Embrace privacy as the default setting to ensure protection of privacy data
- Integrate privacy into the design and embed it into the Organization policy.
- Privacy should be completely functional
- Protect data throughout its lifecycle
- Complete transparency and lawful processing of data
- Prioritize the protection of individuals information
It’s important to assign responsibility to make sure that the end-user privacy is considered. This needs to be done throughout the whole product life cycle and throughout the different business processes. When collecting personal data and processing the data at various levels, an organization should designate an authorized individual to ensure end-user privacy is built into the services, business processes and monitor the privacy posture on an ongoing basis to ensure data protection.
Disclaimer :
“The views and opinions expressed by Ms. Kavitha Srinivasulu in this article are solely her own and do not represent the views of her company or her customers.”
About the Author :

Ms. Kavitha Srinivasulu
Global Head – Cyber Risk & Data Privacy – R&C BFSI
CCISO | DPO | CISM | CEH | CCSO | CCIO| PCSM | PDPP |
Ms. Kavitha Srinivasulu has around 20+ years of experience focused on Cybersecurity, Data Privacy & Business Resilience across BFSI, Financial services, Retail, Manufacturing, Health care, IT Services and Telecom domains. She has demonstrated her core expertise in Risk Advisory, Business Consulting and Delivery assurance with diverse experience across corporate and Strategic Partners.She is a natural leader with versatility to negotiate and influence at all levels.
Ms. Kavitha Srinivasulu is a Board Member of Women in CyberSecurity (WiCyS) India
Ms. Kavitha Srinivasulu is an Executive Committee Member CyberEdBoard Community
Ms. Kavitha Srinivasulu is Bestowed with the following Licenses & Certifications :
https://www.linkedin.com/in/ka
https://www.linkedin.com/in/ka
Ms. Kavitha Srinivasulu can be contacted at :
LinkedIn : https://www.linkedin.com/in/ka
Also read Ms. Kavitha’s earlier article: