2023 USA National Cyber Security Strategy and its
Importance
On March 2, 2023, USA President Joe Biden administration released its 2023 US National Cyber Security Strategy to understand the current emerging trends, managing challenges and to build a digital ecosystem that is more resilient against cyber-attacks. The Strategy recognizes what the US government must seek to protect the critical infrastructures including hospitals, banks, education, manufacturing, and clean energy facilities to protect national security, public safety, and economic prosperity from cyber threats.
The world is gradually increasing more complex and vulnerable threat environment which needs robust changes in the current threat landscape and in handling the ransomware attacks that’s running into millions of dollars in the US as per recent reports. In 2022, the average cost of a ransomware attack was more than $4.5 million, according to IBM report. In United States, private sector technology underlies all essential services open to its citizens to adapt to new changes and growth. However, protecting that space lies within the PPP- Public: Private Partnership space to strengthen the country’s cybersecurity competence and sustain its overall technology Governance strategy. This announcement by the Biden administration signals that the federal government to be determined and build a strong cybersecurity posture.
US National strategy’s vision is primarily focussed on having a more defensible and resilient cybersecurity posture to minimize the impact of cyber incidents and increase the infrastructure security.
- US National Strategy’s five pillars:
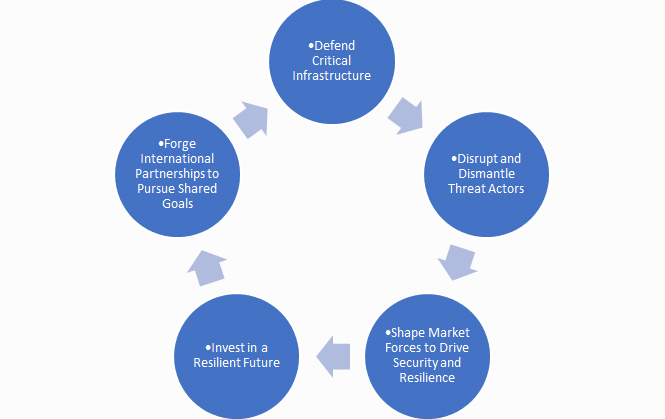
US National cybersecurity strategy has come up with five key pillars to build a resilient digital ecosystem that is built to defend and then attack. A quick overview on the 5 pillars expectations:
1. Defend Critical Infrastructure
Critical Infrastructure Protection and facing critical threats in today’s landscape is highly vulnerable. It consists of actions taken to prevent, remediate, or mitigate the risks resulting from vulnerabilities of critical infrastructure assets and core capabilities. As the risks are evolving with the growth in technology, focus should include changes in tactics, techniques, policies, procedures, frameworks adding on to redundancy dependencies, assets, hardening and guarding etc. To build conviction in the resilience of US critical infrastructure, regulatory frameworks will establish minimum cybersecurity requirements for critical sectors to strengthen current security posture.
2. Disrupt and Dismantle Threat Actors
This strategy focuses on handling malicious cyber actor’s incapable of threatening the national security or public safety of the United States by diligently using applications/ tools to disrupt bad actors, engaging the private sector, and addressing ransomware threats in collaboration with all stake holders .Working across with public and private sectors, the US will seek to address the ransomware threat and disrupt malicious actors. Addressing the ransomware threat through a comprehensive Federal approach and in lockstep with our global strategic partners.
3. Shape Market forces to drive Security and Resilience
Public Private Partnerships and services play a major role in placing the responsibility of building new eco system. There must be various initiatives taken to promote investment in secure infrastructure, liability for secure software products and secured services to protect the environment from most vulnerable threats. This strategy will primarily focus on who can better control cyber threats, including by shifting liability to software products and services.
4. Invest in a Resilient Future
This strategy primarily focuses on strategic investments, collaborative action, extended alliances, and partnerships to lead the world in the innovation of secure and resilient next-generation technologies and infrastructure. Reducing systemic technical vulnerabilities in the foundation of the Internet and across the digital ecosystem will help in building a more resilient business strategies and fight against transnational digital repression. Another key focus area is on building a resilient network to develop a robust national cyber workforce.
5 Forge International Partnerships to Pursue shared goals
The strategy seeks to leverage international coalitions and alliances and bolster defensive strategies to protect against cyberattacks. United States shall also work on leveraging international coalitions and partnerships among like-minded nations to counter threats to US digital ecosystem through joint preparedness, response, and cost imposition. Working with various allies and partners to make secure, reliable, and trustworthy global supply chains for information and communications technology.
All the five pillars provided above are primarily focussed to increase the cybersecurity governance structure, expand regulations of critical sectors, relook into liability frameworks for software security, increase the speed and scale of collaboration with the private sector to disrupt the threat actor groups and harmonize the cybersecurity regulations that apply to businesses.
Whether an organization is in the public or private sector, this National Cybersecurity Strategy will have an impact on upgrading or improving the current cybersecurity posture across critical sectors. Some of the key expectations are:
- Infrastructure Security in the core
- Minimum cybersecurity controls enabled within the organisations.
- Need Data Protection and its regulations complied.
- Protecting technology is a national security essential.
- Private enterprises are a critical dependency for national security.
Emerging trends in 2023 to protect the Data:
- Higher Data Privacy and Regulatory Pressures
- Threat Intelligence replacing huge dependencies on SOC operations.
- End point security priority increases
- Zero Trust replaces VPN.
- Increase of scrutiny in managing Third Parties
- Demand for Cyber Risk quantification increases
- Security on Mobile Devices ramp
- AI & ML need for Data Privacy Increases
- Need for Cloud Security increases in Cloud Computing
Industry Best Practices:
- Develop employee awareness culture within the DNA of the organization.
- Enable restricted access for all employees and implement MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication) to ensure multi-layer security.
- Create a data usage policy.
- Establishing a process for the backup and recovery of essential data.
- Install anti-virus software and keep all computer software patched on an ongoing basis.
- Update operating systems, applications, and antivirus software regularly.
- Reduce 3rd party / supplier dependencies.
- Disable pop-ups, unknown emails, and links to avoid Phishing / Social Engineering.
- Use Data Encryption.
- Use endpoint security systems to protect your data.
- Conduct an Annual Penetration test and Vulnerability assessment.
Currently, regulatory requirements and corresponding compliance burdens are continuing to expand globally, both with respect to applicable standard requirements and sector-specific demands. Adapting to changing regulatory requirements and handling fluctuating compliance obligations is itself now a key part of effective cybersecurity and data privacy governance. The U.S. commitment to international partnerships on cyber issues remains strong, and the Strategy emphasizes working with public and private partners to build a defensible, resilient, and values-aligned digital ecosystem. Evolving shared goals requires a strong global cyberspace where responsible state support is expected and without which it is both costly and isolated.
About the Author :

Ms. Kavitha Srinivasulu
Global Head – Cyber Risk & Data Privacy – BFSI R&C
Tata Consultancy Services
Ms. Kavitha Srinivasulu has around 20+ years of experience focused on Cybersecurity, Data Privacy & Business Resilience across BFSI, Financial services, Retail, Manufacturing, Health care, IT Services and Telecom domains. She has demonstrated her core expertise in Risk Advisory, Business Consulting and Delivery assurance with diverse experience across corporate and Strategic Partners.She is a natural leader with versatility to negotiate and influence at all levels.
The views and opinions expressed by Ms. Kavitha Srinivasulu in this article are only from her personal side and not representing her company viewpoints or sharing any of her customers views.
Ms. Kavitha Srinivasulu is Bestowed with the following Licenses & Certifications :
https://www.linkedin.com/in/ka
https://www.linkedin.com/in/ka
Ms. Kavitha Srinivasulu can be contacted at :
LinkedIn : https://www.linkedin.com/in/ka
Also read Ms. Kavitha’s earlier article:














