Developing Smarter Highways by leveraging Modern Optical Fiber Network
Abstract
In the modern era, ICT (Information and Communication Technology) has become a critical component of designing smart highways. While a lot of emphasis has been given on application layer for making a highway smarter, it is important to understand the criticality of Communication Backbone Infrastructure. Traditionally, all the communication infrastructure were managed by Communication Service Providers and there was very limited rationale for Highway Authorities to get involved in this area. However, the emerging captive needs of Highways has made it important to include network backbone needs at highway design stage. Proper design of Backbone infrastructure will also help in enabling faster launch of next generation service like 5G, Wi–Fi6, Edge Compute etc., along the highways. This paper also seeks to explain the importance of engaging expert agencies for working on all aspects of Optical backbone infrastructure along the highways.
 Key Drivers for Smart Highway Projects
Key Drivers for Smart Highway Projects
Traditionally, highways and expressways were considered the means of high–speed transportation among the cities. However, during recent times it has been realized that highways can act as catalyst of growth for the larger area along the highways. It has also been realized that application of modern technologies like sensing, surveillance, monitoring and analytics can make operations of highways super–efficient and safer to commute. Fast movement of commercial vehicles along the highways helps in overall growth of the economy. Safety along the highways has also become a major cause of concern as large number of fatalities are reported due to lack of discipline like over– speeding, lane cutting, sporadic road damages, etc. In addition to the captive needs of the highways, there has been demand from industries to create enabling framework for Right of way (RoW) permission. Pre–designed Telecom Infrastructure will not only help in meeting the specific needs of Highways, it will also enable Communication industry to contribute in growth of the nation.
Captive Applications for Highway Operations
There are numerous applications being implemented across the world for Smart Highway Projects. Broadly these applications are classified into two categories – Broadband applications and Narrowband applications. Broadband applications require high backhaul bandwidth for sending the data from the site towards the server. Typically, Video based applications comes under this category. Narrowband applications require very low bandwidth for communication purpose. One of the examples of such application is Electronic Toll Collection system. The representative listing of applications under two categories has been done below,
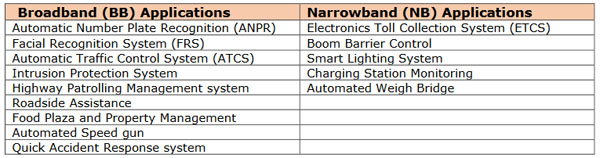
We are witnessing increasing trend of Broadband applications. While NB applications can be supported through 3G / 4G wireless, BB applications require Optical fiber backhaul for good quality services.
Other Requirements
Apart from the captive needs of Highways, there are many requirements which can be met only through the prior consideration at design stage,
1. 5G Infrastructure needs – Unlike previous generations where Tower sites used to support distance of up to 5 Km along the highways, 5G will require cell sites at an interval of every 100 meter (due to very high frequency and bandwidth requirement). Future cars and trucks will have huge number of sensors in–built and will be pushing tera–bytes of data every hour while on the way. To support seamless experience on the way, Highway planners needs to make adequate provision of Space, Power and Optical fiber at shorter intervals. In fact, such requirement will
crop up for the existing operational highways as well.
2. Industrial clusters will require strong connectivity – There will be large number of industrial clusters created along the highways. These greenfield clusters will see implementation of super–efficient factories and warehouses, leveraging the power of Industry 4.0. The entire concept of Industry 4.0 can be operationalized only if very good quality Optical fiber backhaul is made available. This backhaul will have dependency on the Fibre backbone to be created along the highway.
3. Colocation and Edge Data Centre Infrastructure – Modern applications runs on very stringent quality of service norms and ultra–low latency has become the paramount requirement. Latency experience of around 1 millisecond can be achieved only if servers are located in close vicinity to application end point. Hence demand of very secure, redundant, scalable Edge Data Centre Infra will come up at every 50–60 Km distance along the highways. The edge DC will also support the colocation needs of Amplifiers for the Telecommunication links along the highway.
4. Leveraging Highway Network Backbone for offering good quality high speed broadband in surrounding villages – Availability of abundant optical fiber infrastructure on the highways, will reduce the cost of offering high speed broadband in the rural areas by up to 80%. This will help in expediting the government vision of taking fiber to every village of the country.
5. Data Centre Interconnect – The hyperscalers like Google, AWS, Azure, IBM etc. will need hundreds of Data Centers to support exponentially growing data consumption. Data Localization regulation from Government will further fuel the growth. The locations at the end point of Highways are considered the best suited location for creation of new Data Centre. These DCs located in different cities will need large count of fiber from one city to another city for connectivity purpose. Availability of fibre will spur the growth of Data Centres in various cities connected through highway. (It is noteworthy that our Prime Minister terms the Optical fiber backbone as the i–way, meaning information superhighway).
Benefits to Highways and Government
1.Faster implementation of concept of Smart Highways for ensuring safety and efficient operation.
2. Transportation Cost reduction by eliminating the inefficiency in the operation
3. Additional source of revenue by monetizing optical fibre and colocation infrastructure
4. Major contributor in achieving Digital India vision of government
5. Enabler of next generation of Telecom Technologies along the highway.
6. Availability of cost–efficient fibre on non–discriminatory basis will create competition in Telecom market. New Small operators, Internet Service Providers and Virtual Network Operators (VNOs) will also proliferate in the Indian telecom market.
7. Growth of Data Centers in different cities located along the highways
Key Considerations for creating a good Telecom Infrastructure along Highways
The optical fiber infrastructure being planned along the highways is expected to support the backhaul and interconnect requirement of various technology elements like that of 5G, Wi–Fi, XGSPON, MPLS, DWDM, OTN etc. The placement of the network elements of these technologies varies significantly because the different architecture. Hence it is important to have very good understanding of all technologies to ensure that future proof and scalable infrastructure should be designed which can meet all current and future requirements of the Communication providers and Highway authorities. Few critical considerations for designing any Optical fibre infrastructure along the highways are as follows–
- Position of OFC duct – Whether the duct should be placed along the edge or at the median of the highway. Various pros and cons associated with each approach has to be take into consideration along with recommended design for each scenario.
- Whether HDPE ducts should be placed by digging a trench and burying it. Alternate option can be creation of utility ducts and allocation of space for Telecom Utility.
- Approach for managing the ducts of different tenants like Telecom service providers, Infrastructure Providers, Enterprise service providers etc.
- What should be the fibre count in the OF cable to be laid for captive use of NHAI and what should be the approach for managing the OFC network of NHAI?
- Various KPI and SLA for maintenance of OFC and duct infrastructure.
- Recommended Distance between the Manholes and Chambers along the utility duct. In traditional design, distance between two chambers used to be 2 Km in most of the cases. However, in the 5G era, the tapping of the fibre will be required at every 200 meter and hence tapping chambers will have to be designed accordingly to avoid rework at later stage.
- Design of Colocation infrastructure for placement of Regenerator and Edge DC. This infrastructure will need secure space to house minimum 10 rack space, DG sets and Power back up. Such colocation space will be critical for supporting active infra along the highways.
- Pole infrastructure – As 5G services will need Radio Unit placement along the highway at typical interval of 100 to 150 meter, adequate space and power facility will have to be planned.
- Cabinets for supporting Electronics and Passive Elements – Different design of cabinets with adequate IP rating (IP65, IP67 etc.) will have to be placed along the utility corridor. These cabinets may house passive components like fiber patch panels or active elements like switch, router, Radio Units etc.
- Approach for placement of road crossing at defined interval for supporting fiber crossings along the highway.
- Design considerations for enabling breakout of OFC ducts and Cables from the highway utility corridor for extension towards various clusters like Industrial Clusters, Residential Clusters, Adjoining Villages, Food Courts, Commercial Complexes etc.
- Monetization models for OFC, HDPE ducts, Poles and Colocation infrastructure.
- Approach for asset management like Dark fiber, Cabinets, Poles, HDPE ducts etc. There should be proper approach for monitoring the allocation and utilization of various assets along the utility corridor.
Conclusion
The highways of future will be very different from that of the past. In order to reap the benefits of emerging and future technologies, infrastructure support to communication providers from NHAI will be crucial. Design, Deployment and Management of Optical Fibre Infrastructure are very specialized jobs and require involvement of deep domain experts. These experts should not only have very good understanding of optical fibre infrastructure, but should also have deeper understanding of emerging and future network architecture of technologies like 5G, Cloud, Hyperscale Data Centre etc. Involvement of such expert will help in designing the future proof, secure and scalable Telecom infrastructure and will enable the vision of making highways truly “Smart”.
About the Author:
Mr. Himanshu Kumar
Chief Technology Officer
![]()
Technavious Solutions Private Limited.
Mr. Himanshu Kumar is a Tech Leader & Telecom Professional with extensive experience in Design,Build and Management of Large Scale Fixed line and Wireless Networks. Starting his career as Indian Telecom Service officer in 1999, he has held several senior positions in companies like STL, Bharti Airtel, BSNL and DoT. He has filed several patents related to design of OFC and Data Centre Products and Solutions. In the last stint he was heading the Global Technology team of the Network Service division of STL.
Himanshu is passionate about the power of Digital technology and has firm belief that Quality of life can be improved significantly by “Bridging the Digital Divide”. Currently. Himanshu is working on building a Technology start-up which has plans to make big contributions in design, build and management of large scale Optical fiber and Data Centre Infrastructure.
LinkedIn : https://www.linkedin.com/in/km
Twitter : https://twitter.com/kmrhimansh









