The Rise of Mobile Robots in Warehouses : What Perks
Await Robotic Engineers?
Summary: Mobile robots are becoming more commonplace on the factory floor due to rising labor costs and staff shortages. As a result, the demand for robotics engineers will likely continue growing in the coming years, providing an exciting path for people seeking career stability
The last few years have seen robots move from a novelty solution deployed by large companies to a mainstay technology used across various sectors. Many types of mobile robots have emerged, each bringing tangible benefits to large and small operations in the logistics industry. These trends have fueled the need for professionals capable of designing and handling automation technologies for improved productivity, enhanced safety, and lower operating costs.
 The Rising Demand for Robotic Engineers
The Rising Demand for Robotic Engineers
There’s never been a better time to explore career opportunities in robot engineering. The rapid growth of e-commerce and the marked scarcity of available workers have pushed the industry to adopt more robotic solutions. According to a Gartner study, roughly 75% of enterprises will use robotic automation in their warehouses by 2027.
This corresponds with the growing demand for engineers specializing in mobile robot design to address evolving supply chain needs. Research shows there will be nearly 20,000 new robotic engineering jobs by 2029. There are several benefits to pursuing a career in this field.
Job Security
Robotics has many applications across various industries, providing ample employment and career growth opportunities. At the same time, the United States is facing an acute shortage of high-tech engineers.
The country will need 400,000 new engineers every year to meet current demand — and who knows what the demand level will be in the next decade? However, this presents job security and unlimited growth potential for people in the field as society becomes more dependent on technology.
Good Pay
According to Payscale, the average robotics engineer’s annual pay starts at $81,743 for entry-level positions in 2024. This figure rises to around $106,992 per year for more experienced personnel.
Salary estimates from Glassdoor are even more generous, with projections reaching over $150,000 annually on average. Amazon, Tesla, Apple and Meta are the top companies hiring mobile robot design specialists.
Creative Work
A career in robotics engineering involves designing complex systems to solve unique problems. Many find this creative freedom fuels their passion for the job, allowing them to express themselves freely within the confines of the project requirements.
Solving unique problems also provides a sense of fulfillment. The process allows a full creative circle where engineers identify challenges, imagine solutions and create designs to address them.
Job Satisfaction
Robotics engineers are some of the happiest tech workers around. A recent survey shows these professionals rate their career happiness 4.2 stars out of 5, ranking above related disciplines like nanotechnology and photonics engineering. When asked to rate their jobs based on meaningfulness, 46% gave 5/5 stars — only 4% gave a 1-star rating.
Abundant Certification Options
Becoming a robotics engineer requires at least an undergraduate degree. However, many certifications can ramp up an individual’s qualifications and proficiencies, allowing them to pursue specialization. Additionally, several institutions and private organizations offer scholarships to encourage enrollment in engineering courses.
Robotics Engineering Tasks
Robotics engineers are highly skilled mechanical engineers who design and maintain robots and their electronic systems. They use their knowledge of technology to research and develop the processes necessary to operate robotic systems efficiently and reliably.
Those in this position must understand robot construction and distribution expenses. They also assist and supervise other technicians in building, configuring and troubleshooting these systems.
Usually, robotics engineers work traditional business hours. However, some shifts may vary, especially in round-the-clock warehousing and logistics.
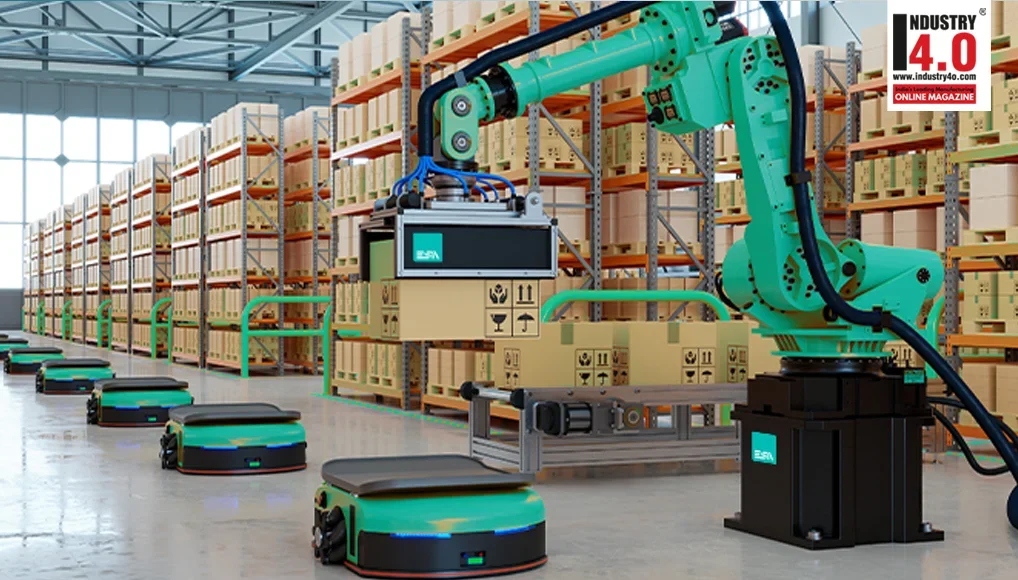
The Role of Mobile Robots in Warehouses
Automation in the warehousing sector has become necessary thanks to the increasing demand for flexibility, scalability and speed. This has been the case since the COVID-19 pandemic forced everyone indoors, increasing reliance on e-commerce. Sticking to manual processes can harm warehouse productivity, as they are costly and often error-prone.
Hence, many types of mobile robots have come about in the industry. These autonomous devices offer a scalable solution to daily operations across the materials storage and logistics value chain.
Mobile Robotics Main Applications
Unlike stationary bots — such as articulated robotic arms confined to specific locations — mobile robots boast remarkable adaptability to various environments. This flexibility and maneuverability enable them to accomplish different tasks, making them particularly valuable in warehousing.
The most significant benefits of employing robots on the factory floor include:
Reduced costs: Warehouse workers must receive salaries and benefits. On the other hand, robots don’t require wages, making them a cost-effective solution for minimizing operating expenses.
Increased productivity: Robots don’t need breaks. They can also work around the clock without the potential for human error.
Improved safety: Today’s autonomous mobile robots can handle picking, storing and packing goods without manual intervention. This means fewer human workers dealing with dangerous items or heavy equipment.
Enhanced scalability: Robotic solutions can easily scale up to meet changing demand, providing greater flexibility and agility in warehouse operations.
Real-time data and insights: Advancements in Internet of Things technology allow robots to provide actionable insights that improve throughput in order fulfillment.
4 Types of Mobile Robots Automating Warehousing
Experts classify the various types of mobile robots used in warehouse automation by the tasks they fulfill, such as the following four modalities.
1. Goods-to-Person
These robots carry items or an entire rack to the person picking goods. The selector can choose the item they need and the robot will return the rack to its original position. A goods-to-person mobile robot reduces the amount of walking for warehouse workers, which can be highly beneficial in large environments.
2. Commercial Floor Cleaning Robots
As the name suggests, these robots ensure clean, sterilized floors in commercial spaces. They’re crucial in warehouse operations, handling and storing hazardous materials, and ensuring the area is safe for human movement. Commercial floor-cleaning robots use autonomous navigation systems equipped with state-of-the-art sterilization devices for efficient cleaning throughout the facility.
3. Collaborative Robots
Popularly called cobots, these mobile robots follow warehouse associates around, providing any needed support. For example, they can scan items to confirm they’re in the right place, transport heavier goods and group similar tasks. Automated cobots can make warehouse operations up to 2.5 times more productive, helping bridge industry labor shortages.
4. Autonomous Forklifts
Autonomous forklifts can do everything a traditional forklift can do without human intervention. According to the National Safety Council, there were 73 work-related forklift deaths and 15,480 injuries resulted in absenteeism in 2022. In this way, these machines can take over the most labor-intensive operations in a facility while enhancing safety.
As the underlying technology behind mobile robots continues to advance, more warehouses and distribution centers will likely adopt them for daily use. Research shows over 500,000 global mobile robot shipments are expected by 2030.
Prep For a Career in Mobile Robot Design
The rise of mobile robots in warehouses is driving demand for robotics engineers. This career path can provide several benefits, including a high-paying salary, job security and excellent growth prospects. Simultaneously, this role requires curiosity and initiative as newer technologies emerge and mobile robots become increasingly integral in optimizing supply chain management.
About the Author:

Emily Newton
Editor in Chief
Revolutionized
![]()
Emily Jade Newton is the Editor-in-Chief of Revolutionized a popular science publication that dives into the latest innovations in science, technology and industry.
Emily Newton is an industrial writer who enjoys showcasing innovation in her stories.
Emily Newton specialize in writing in-depth articles and blog posts for the industrial and sci/tech sectors.
Emily Newton enjoys researching the latest trends and optimizing articles to perform better in search engines.
Emily Newton can be Contacted at :
e-mail | LinkedIn | FaceBook | Twitter | YouTube | Pinterest | Website
Also read Emily Newton‘s earlier article :