Industry 4.0 – An Intro to the Fourth Industrial Revolution
Industry 4.0 as a manufacturing movement is reshaping the business of building products. Fueled by unparalleled machine intelligence and connectivity, industry 4.0 introduces Cyber-Physical Systems and IoT on the Assembly floor. Our modern manufacturing efforts are driving advancements in industry 4.0, bringing greater efficiency, quality and sustainability to the manufacturing process.
The shift to smart factories is already well underway. While robots performed a global average of 10 percent of factory tasks in 2015, by 2025, that number is expected to rise to 30 percent and as high as 40 percent in some sectors. Some automated additions will free up employees for more engaging tasks, while others will work alongside them to perform the tasks that are too difficult/mundane/arduous/unsafe for humans to perform repeatedly.
 What Does This Mean For Manufacturing Companies?
What Does This Mean For Manufacturing Companies?
Mounting challenges face the manufacturing sector with a major focus on optimizing production and balancing costs. Rapid advancements in emerging technologies such as the industrial internet of things (IIoT), advanced mobile robots, additive manufacturing, industrial connectivity, and artificial intelligence-enabled solutions enable companies to tackle these challenges head-on by choosing the most suitable technologies to invest in. As technology progress continues, it is important for factories and production facilities to be proactive and identify potentially disruptive changes at an early stage.
In the era of industry 4.0, companies must design and engineer intelligence and sustainability into both the things they make and the processes for making them.
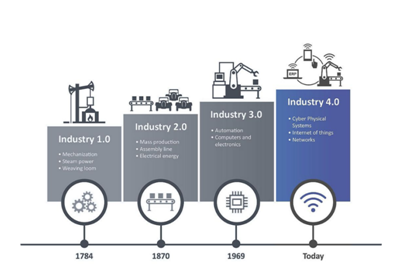
Trending technologies to build the smart factory of the future :
1. Enhanced visualization and advanced simulation
Manufacturing line layouts and testing requires time, resources and capital, only to potentially result in waste – unless those operations can first be simulated. Simulation enables us to observe operations on an object or environment without having to physically perform that operation which may damage tangible objects.
Simulation seeks to take advantage of the “digital twin”, or the digital representation of a physical object. It is often performed during the design phase or before a factory becomes fully operational to see how changes in equipment specifications, scheduling, downtime and maintenance can affect a process throughout the duration of its life cycle.
As software on your computer simulates the actual environment and provides an optimal solution, that solution can then be reflected in the physical environment to create a closed loop cyber-physical system.
2. Additive manufacturing
The traditional product development cycle meant waiting anywhere from days to weeks for a completed functional prototype. The advent of additive manufacturing and 3D printing has transformed that process, streamlining the early phases of product development at a fraction of the time and cost.
While prototypes and concept models can visualize your future product, the advantages of additive manufacturing are not limited to the design phase. Scaling 3D printing into production means you can easily customize the product for each user and minimize material usage to lower the overall cost of the product. What’s more, parts fabricated on demand mean reduced lead times and minimal buffer inventory – and that makes for simpler, easier supply chain management.
3. Smart Automation
It’s no longer about a robot arm assembling a product – now that robot arm can feed data into the cloud to give you better insights into your operations.The next generation of robots will have sensors that enable them to pull information to better perform their tasks. In return, you’ll be able to achieve greater operational efficiency and predict your production output with more confidence.
Collaborative robots, or “cobots”, are able to perceive their environments more effectively. They use sensors to perceive their environment to see if a human is working next to them. If they’re getting too close to a human, they can automatically stop. It’s safer to work with them and better for workers because they perform the tasks that are too difficult or strenuous to perform repeatedly.
4. Machine-to-Machine Communications
At the heart of Industry 4.0 and modern manufacturing, machine-to-machine (M2M) communications are the key to unlocking factories of the future. Traditional hardwired connections between machines on the manufacturing floor are not designed for connectivity, which means these machines inherently require manual assistance from an operator. Machine-to-machine communications present the first real opportunity for touchless line maintenance, and one step closer to a fully automated manufacturing environment.
Implementing machine-to-machine communications can free up our manufacturing line operators for more value-added work. Manned by a single operator, e-dashboards monitor manufacturing processes and provide real-time data analytics, reassigning an otherwise monotonous task. Establishing the M2M lines resultin significant savings every month.
5. Augmented Reality
The augmented reality market has exploded in recent years, with more than 150 companies in multiple industries, including 52 of the Fortune 500, testing or deploying AR/VR solutions. Use cases have extended beyond the traditional perception of gaming and into enterprise applications. Industrial and manufacturing environments have enormous opportunities to use augmented reality to optimize their operations.
One way we can use augmented reality in our modern manufacturing processes is through remote assistance. Imagine having expert guidance at your fingertips every time you needed it in starting a new process or issuing a repair. An operator faced with fixing a machine on the line can connect with experts across the globe using augmented reality, displaying his field of vision for them to view and guide appropriately.
6. Cloud
Introducing IoT on the factory floor requires seamless connectivity and a limitless repository of data. Cloud computing enables you to extract, analyze and store information that may affect the production line.
Connected machines could increasingly be able to self-report problems and provide insight on ways to improve efficiency, improving quality and yields. Smart robotics capable of capturing production data can use those insights to predict downtime and prescribe corrective action accordingly. Data from augmented reality will have a significant impact on research and development, giving consumers more of what they want, getting it to them faster and cutting down on costs—a system that ultimately will drive innovation.
The deluge of data presented by machine-to-machine communications, smart robotics and augmented reality calls for computing environments with rapid scalability. Building from one of our reference designs or integrating off-the-shelf components with our system integration capabilities are two ways to accelerate development and speed your time to market.
Industry 4.0 is here with exciting opportunities and challenging new requirements. You want to partner with an organization that can address the manufacturing complexities of this new era and also take advantage of advancements to bring new ideas to life.
The most crucial step toward implementing Industry 4.0 involves the integration of pre-existing business systems such as the following:
Computer Aided Drafting (CAD)
Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM)
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)
Ideally, the manufacturers that seek to make the transition in the immediate future should focus internal resources on the innovations required for the change. However, manufacturers currently encumbered with successive IT cycles are liable to lag in the transition, as funds are primarily spent maintaining current systems. While this maintenance might seem necessary, forecasters predict that this could leave the manufacturers that adopt slowly at a competitive disadvantage in the long run.
Manufacturers of all sizes and ages could benefit from the implementation of Industry 4.0, which could ultimately prove to be a game changer as underdogs adopt and soar to the front of the pack, and established companies lag and struggle to stay relevant. Over the next decade, Industry 4.0 might turn little-known companies into the new industry leaders.
About the Author

Mr. Atul Punj
Head – North America Sales
Brila Soft – CK Birla Group
He can be contacted at
LinkedIn : https://www.linkedin.com/in/at
Twitter : https://twitter.com/AtulPunj5
email : [email protected]