Roll Over AI, Synthetic Intelligence SI is here
Is Synthetic AI Data poised to take over AI Data? Is AI nearing the end of product life cycle …
Synthetic Intelligence (SI) is intelligence that is artificially constructed and seeks to imitate and surpass human reasoning and creativity. SI includes design of flexible systems that can function in learning, reasoning, decision making and creative problem-solving. Synthetic Intelligence is about a built or engineered nature.
 SI does not emerge into being biologically but is synthesized from algorithms, data, and computational models. Synthetic intelligence directly addresses the artificial aspect of artificial intelligence. SI explains that intelligence of machines is not always an imitation of that which is artificial, and it may simply be genuine intelligence.
SI does not emerge into being biologically but is synthesized from algorithms, data, and computational models. Synthetic intelligence directly addresses the artificial aspect of artificial intelligence. SI explains that intelligence of machines is not always an imitation of that which is artificial, and it may simply be genuine intelligence.
So, what is SI, how will it impact technology, and the manner in which we consume tech, what are some examples, will SI replace AI? This blog answers these questions.
What does SI basically do
AI is about learning through data and using the findings to create movies, images, songs, and serve the industry. However, gathering this data is a tremendous task and subject to privacy laws. Finding data is the biggest challenge.
SI overcomes this challenge. In its most simple form, SI is about generating synthetic data, based on real data. It studies the patterns of data elements and then generates large data sets that are used by various sectors. The data is “fake real” meaning that it is fabricated using real data.
Now, the main task of finding usable data is done. AI engineers can focus on building accurate predictive AI systems. Existing machine learning, data analysis, can be used.
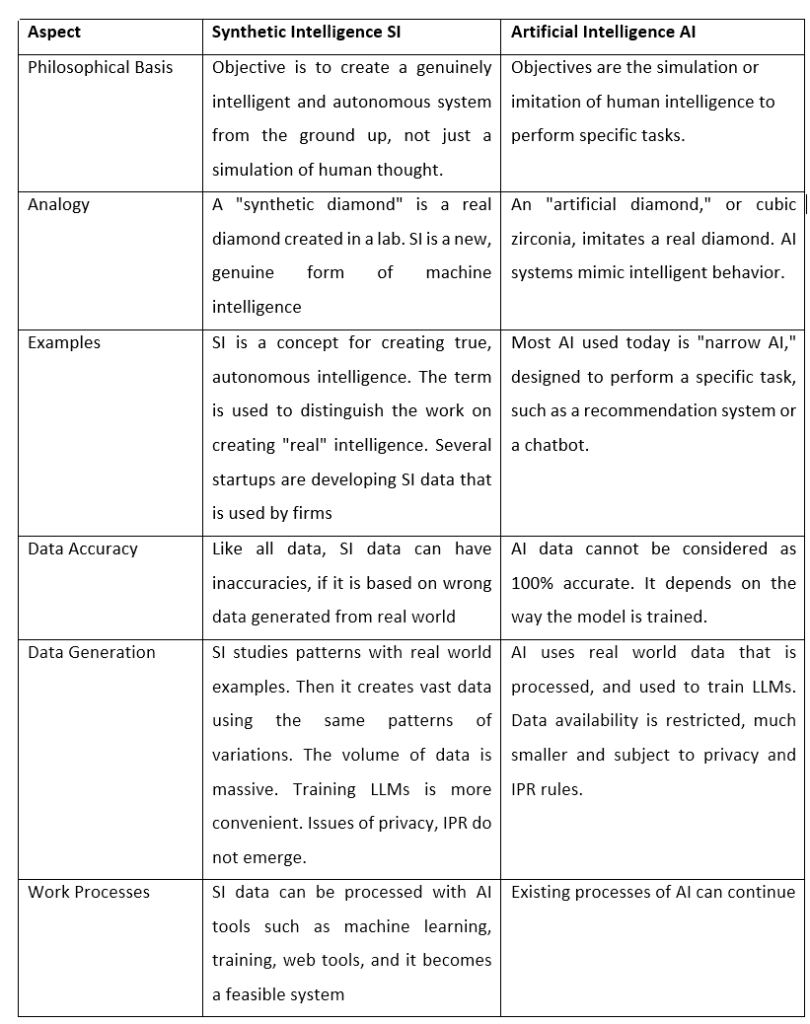
Differences between SI and AI

Image Credit: Shashi Kadapa with Google Gemini
Some important differences between SI and AI are given in the following table.
Key Aspects of Synthetic Intelligence
John Haugeland, an American philosopher of mind, cognitive science, phenomenology, and Heidegger. He explained about SI in 1986, giving an example of synthetic diamonds to explain the concept of SI.
Synthetic diamonds are not ‘diamonds’, but they are considered as diamonds. These are created by synthesis where parts are combined and processed to whole part, but they are human versions of naturally produced diamonds.
The important aspects of SI are:

Image Credit: Shashi Kadapa with Google Gemini
Synthetic Data as the Impetus: Current AI systems often depend on data, but there is limited access to high-quality, diverse, and unbiased datasets. Synthetic Intelligence uses synthetic data, or computer-generated datasets, as a safe and scalable way to train models. This is especially important in sensitive areas such as healthcare, financial use cases, or defense where real data is difficult to obtain or limited by law, regulation, and ethical considerations.
Synthetic Media Production: Synthetic Intelligence in its media form has some of the most recognizable face through its ability to create synthetic media. This includes graphics, video images, audio, and even synthetic digital humans. These capabilities work together to power large sectors, such as entertainment media, advertising, education, and simulation training.
Cognitive Simulation: An important aspect of Synthetic Intelligence is to simulate cognition. This would mean building systems that perform not only can process data, but also reason, plan, and adapt. This is one pathway to what researchers have called Synthetic General Intelligence (SGI)—a system that has cognitive flexibility as humans do.
Human–AI Dyads: Synthetic Intelligence must not replace human intelligence, rather it has the potential to become a co-intelligence that augments human intuition, creativity, productivity, and in some cases, decision competence. Together human intuition and synthetic reasoning can probably change the way organizations innovate.
PSI theory applied to SI
PSI theory, developed by Dietrich Dorner et al., (2013), is the first architecture that addresses cognition in a more holistic way. Joscha Bach in his book speaks about Principles of Synthetic Intelligence – PSI as applied to SI. Computational models of cognition provide a limited scope of cognition. They address contexts related to problem solving and reasoning, and treat perception and motivation as unconnected.
It extends the conceptual link between motivation and emotion and perception and reasoning, and advances a grounded neuro-symbolic representation of cognition. Psi makes a major contribution to an integrated understanding of mind by demonstrating the conceptual links between perception and memory, language and mental representation, reasoning and motivation, emotion and cognition, autonomy and social behavior.
However, Joshua explains that PSI’s development in psychology, its methodologies and documentation have limited its impact. The author further develops the Psi theory to cognitive science and artificial intelligence. He has integrated the theory and technical structure of the theory into context and to clarify how the terminology of Psi contributes to our understanding of cognition.
What are the applications of synthetic intelligence

Image Credit: Shashi Kadapa with Google Gemini
Synthetic Intelligence (SI) is rapidly developing as a serious contender to several startups that are developing, SI-based products. The appeal of SI is creating high quality synthetic/artificial data that reduces bias, protects privacy and IPT, reduces sully collection time, cost, and availability of technology to many.
SI innovations are utilized for image generation, 3D simulated environments, and structured data modeling. StartUs presents a list of leading startups that are providing SI solutions are Simulacra Synthetic Data Studio – AI-powered Synthetic Data Platform; Sightwise – Machine Vision-based Synthetic Data; brewdata – Synthetic Data Generation Platform; Synthera AI – Synthetic Financial Market Data; and others. SI data is utilized by multiple sectors.
A few of the sectors are:
✦ Healthcare: SI technology is utilized in disease diagnosis to analyze medical data to help diagnoses diseases such as cancer and disease drug discovery.
✦ Chatbots: Advanced chatbots use SI analytics to interpret context based on user input and provide tailored, personalized support that can be used for enhancing engagement.
✦ Autonomous and adaptive driving: Self-Driving Cars use SI to make decisions and navigate complex situations without an onboard human. Space exploration- unmanned spacecraft use SI systems to adjust and account for unforeseen circumstance and make critical decisions on their own.
✦ Predictive Analytics: SI systems are were utilized traditionally for analyzing market reactions to online purchasing. By creating and utilizing a SI algorithm to analyze the behavior systems can individualize marketing. SI systems are also utilized in environmental forecasting by developing its own models predicting weather patterns, or natural disasters.
✦ Marketing agencies: Marketers are utilizing SI to understand customer behavior, testing ads, and improve targeting. Since it does not consider actual personal data, we can keep it highly private by using synthetic data to convert proprietary data to outcomes using a specific SI model etc. still helping agencies create smarter and more personalized marketing strategies
Will SI replace AI
Not really and in the absolute sense. Lee (2025) in his article, discusses the idea that SI is the paradigm of AI of the future. Critical technical and legal issues are challenged to AI by the necessity of acquiring large real-world data sets to train the machine learning models.
Obtaining such real-world data can be extremely challenging and can risk privacy, add in bias in automated decision making, and engage in mass copyright infringement. SI is paradoxical as a technical construct in the sense that it can mitigate many of these risks, but not eliminate them.
Data scientists are compelled to use simulated driving environments, invented medical records, falsified images, and all forms of synthetic data to train the machine learning models. Artificial data, in essence, is being used to train artificial intelligence.
Synthetic data has many technical advantages, and several legal ones as well. It heralds dramatic reductions in the costs of acquiring data, eliminates privacy issues, decreases the possibility of automated discrimination, and diminishes copyright issues.
Equally as promising, however, synthetic data also presents significant threats. Synthetic data and its deficiencies in the development and deployment of synthetic data can exacerbate the dangers of AI and social harm. Accordingly, SI is an innovation ecosystem to advance its responsible and robust development.
As a result, SI will ultimately become a new form of AI that is cheaper and more straightforward.
Summing Up
The blog examined key aspects of Synthetic Intelligence SI with AI. The findings indicate that SI generated data can be used cost effectively to replace AI data that is difficult to procure and subject to privacy laws.
So, will SI replace AI? Yes, at least the data generation, processing, and machine learning part that is most challenging. SI data is accurate, reliable, but subject to the same accuracy issues of AI data. The process of data generation, processing, training LLMs is simpler.
Present AI engineers do not have to fear about redundancy. They need to retrain and adapt. Well, we all have to do that anyway.
Legal Disclaimer: The views, thoughts and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not reflect the views or positions of INDUSTRY 4.0. The content is provided by the author as-is and is published solely for informational or educational purposes.
INDUSTRY 4.0 does not guarantee the accuracy, completeness or usefulness of any information presented and is not liable for any errors, omissions or outcomes resulting from the use of this information. The responsibility for the content lies entirely with the author.
About the author :
 Mr. Shashi Kadapa
Mr. Shashi Kadapa
Based in Pune, India, Mr. Shashi Kadapa is an engineer, MBA and has worked with leading IT and manufacturing firms. A multi-hyphenate, he has roles as a technical writer, and SEO content writer with a focus on IT and tech topics.
Creative fiction is his passion, and he serves as the managing editor of ActiveMuse, a journal of literature. His stories across multiple genres are published in more than 45 US and UK anthologies.
Mr. Shashi Kadapa can be contacted at :
E-mail | LinkedIn | Blog | Mobile : +91 7387492371
Also read Mr. Shashi Kadapa earlier article:














