Workflows are key to any business process, which defines a pre-defined execution path with a set of well-defined steps with conditions and rules as needed. Every business has certain set of processes which they need to follow and execute every day to run the business, but major part of it might be executed manually or decisions are taken on ad-hoc basis based on personal experience of the person who is executing an activity. Also, there may not be always a digital model of the process maintained, and the users need to rely on experience and paper-based documentation to execute and analyze the process.
With Industry 4.0, digitalization of process and introduction of cyber-physical systems enables automation and real-time access to data for intelligent decision-making. Intelligent workflows not only helps in digital modeling of processes, but also enable Intelligent analytics, decision-making and process automation. As and when required, this also uses exponential technologies such as robotic process automation (RPA), intelligent chatbots, predictive and prescriptive analytics, IoT, Blockchain and so on.
As an example, consider the process of manufacturing a special purpose machine designed and manufactured by a company in engineering industry. This is a complex manufacturing scenario where the product is completely designed, configured, and assembled based on specific customer specification. The process starts with the customer enquiring for a product with a specific set of requirements which is the lead generation process which triggers the engineering and product design process through a project system created for complex products with multiple parts and sub-assemblies which need to be designed, configured or procured based on the specifications provided within a defined cycle time. After the initial design the product price quotation is created and through an approval/review process it is converted to a sales order. Once the customer accepts the same., this triggers the manufacturing process which involves the detail product design, production planning, manufacturing execution and assembly, procurement and subcontracting and finally installation and commissioning of the product at the operations site which is usually done for large equipment. This in turn leads to the service initiation, billing and finally the after-market service operations to provide continuous service as per the contract and warranty conditions.
Here as we see the end to end process which consists of multiple sub-processes such as Lead to Order, Complex Assembly & Manufacturing, Handover & After Market Service. All of these are interconnected to each other with multiple granular sub-processes under them, spanning across different IT systems and departments inside the organization and even beyond.
Assume if a product issue is reported during the operation of this special purpose machine in field, the OEM will like to find the root-cause of the problem which may be due to a specific design consideration, or specific components procured from a specific vendor, or a specific issue during manufacturing of the product. Now with the absence of a process model and digital thread it may not be possible to easily trace back to the root-cause of the problem as this involves many manufacturing stages, multiple subcontractors and vendors. With Industry 4.0, the above issue can be easily addressed by two parallel approaches namely – defining the digital process model for the end to end process and introducing IoT and digitalization as much as possible leveraging the exponential technologies. This will in turn enable to realize the digital thread across the process-chain which will not only provide end to end visibility of the process at any point of time, but also using the data mined across the process to enable automation and process improvements with intelligent actions and helping to reduce cycle time and improve product quality and customer satisfaction.
At different steps of this value-chain, certain intelligent actions can be infused levering the exponential technologies and Industry 4.0 concepts.
For example in lead generation process, intelligent bots can be developed to consume the news and stock information to determine the potential customers who might be starting an expansion or modernization initiatives for their manufacturing facilities and need specific equipment depending on their business need. Intelligent chatbots can be used to validate the demands with the customers and automatically generate sales lead which triggers the engineering design and project creation based on the previous customer data and derive pricing of the product intelligently by cognitive analytics.
Once the quotation is approved by the customer, sales order is created automatically through the intelligent workflow and triggers the planning and manufacturing process which also should implement the cognitive planning process and intelligent procurements processes to determine the most optimized planning and procurement or subcontracting options, considering the various factors such as environment, transportation, cost, reliability, etc.
Intelligent workflow can also help in intelligent trigger of preventive actions before asset breakdown happens or nonconformance happens in shop resulting in quality rejection.
Intelligent workflows can also be triggered from supply chain control towers when an end to end process KPI shows unacceptable performance and hence provides quick proactive action to bring back the process performance to intended values.
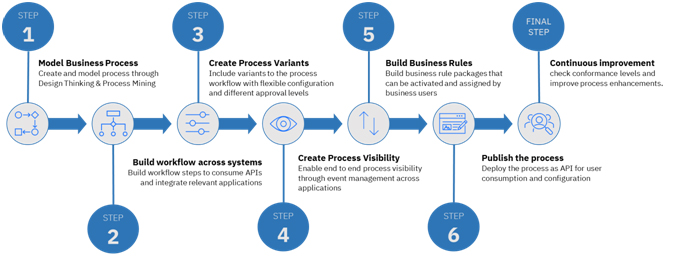
To define Intelligent workflow for such a complex manufacturing and After service set up, following steps, need to be followed as shown in Figure
- Model the process and sub-processes by Design Thinking workshops with end users and process mining across relevant systems by using specific tools available for the same
- Develop the actual workflows based on the process model across the IT systems levering cross-system workflow management tools. Infuse intelligence and automation using the exponential technologies wherever possible
- Create the process variants if needed to address different variations of the process
- Define the process KPIs across the workflow
- Define and create business rules which provides flexible rule management by end users to control the processes
- Publish the process as APIs for easy consumption by end users and from different triggering points
- Use the process KPIs and feedback from end users to continuously improve the process
Intelligent workflow is the most promising approach to deliver value from organization’s industry 4.0 initiative. It will be wrong to assume this just another new technology as this is a new way of working. As Industry 4.0 concepts are getting extended beyond shop floor increasingly with emerging domains like Logistics 4.0 or Procurement 4.0 – Intelligent workflow can also be adopted for processes beyond manufacturing like Procure To Pay, Order To Cash and Record to Report.
About the Authors

Mr. Rajesh Ray is an Associate Partner & Lead – Digital Supply Chain Practice @ IBM India Pvt. Ltd.,
He is an Engineer + M.B.A. and have 23 Years of consulting and domain experience in supply chain. He had worked in manufacturing and supply chain domain in ITC and Exide Industries. He started his supply chain consulting career with i2 Technologies followed by SAP AG in Germany and for last ten years with IBM. Rajesh is author of three books and 55 articles in different supply chain journals. He is honorary member of CII Logistics and SCOR society.
Mr. Rajesh is an IBM Industry Academy Member, Adjunct Professor of IIT Kharagpur, Principal Digital Supply Chain Architect – PMI, Global Logistics Innovation Lead – Nestle and is a frequent speaker in different supply chain forums.
He can be contacted at:
Mobile: + 91 9830678171 | E-Mail : [email protected]

Mr. Dipankar Saha
Principal Architect (Industry 4.0)
Incture Technologies![]()
Mr. Dipankar Saha is an IT Architect having 20+ years of experience with specialization on Industry 4.0 & IoT solutions, SAP Manufacturing, Microservices & Cloud Applications Development and Intelligent Workflows.
He is experienced in defining architecture and leading implementation of Industry 4.0 solutions for manufacturing execution, analytics, and integration and has led several large and complex Industry 4.0 implementations globally as well as worked on product development.
He has co-authored several professional books on SAP Manufacturing solutions (SAP MII, ME, OEE) which have been published from renowned publishers e.g. SAP Press, Apress & WisPubs and published whitepapers in online journals.
Currently he works at Incture Technologies as Principal Architect.
Mr. Dipankar Saha is Bestowed with the following Licenses & Certifications :
https://www.linkedin.com/in/di
Mr. Dipankar Saha can be contacted at :
Also read Mr. Rajesh Ray earlier article :










