Industry 4.0: The Future of Manufacturing
Industry 4.0, also referred to as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, characterizes the present trajectory of automation and the seamless exchange of data in the realm of manufacturing technologies. This phase of the Industrial Revolution strongly emphasizes interconnectedness, automation, machine learning, and the utilization of real-time data. Industry 4.0 represents a fundamental shift in how companies manufacture, enhance, and disseminate their products. The digitalization of manufacturing processes brings about a profound transformation in the production of goods. Industry 4.0 transcends the mere adoption of new technologies and tools to enhance manufacturing efficiency; it entails a revolutionary overhaul of businesses’ entire operational and growth strategies.
Recently, there has been a growing conversation within the industry regarding a more advanced iteration of Industry 4.0, known as Industry 5.0. Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0 represent distinct phases in the evolution of industrial processes, each ushering in novel technologies and methodologies. While Industry 4.0 primarily revolves around integrating machines and IT systems, Industry 5.0 takes a step further by amalgamating the capabilities of human workers and machines to harness and augment their respective strengths synergistically.
Here are some key differences between Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0.

Focus: Industry 4.0 focuses on making manufacturing processes more automated and digital, while Industry 5.0 focuses on combining the unique strengths of humans and machines to create more flexible and personalized manufacturing.
Technology: Industry 4.0 is built on a foundation of technology, automation, and data analysis, while Industry 5.0 further evolves this foundation to incorporate customization and innovation in production.
Human Factor: Industry 4.0 centers on the digital integration of machines and IT systems, while Industry 5.0 aims to synergize the roles of humans and machines to amplify their unique capabilities.
Sustainability: Industry 5.0 emphasizes sustainability and personalization in manufacturing, aiming to produce exactly what consumers need, eliminating waste, and reducing environmental impact.
Collaboration: Industry 5.0 emphasizes closer human-machine collaboration through cyber-physical systems and technologies.
Industry 4.0 Advantages:
Industry 4.0 offers several advantages to manufacturers, including:
Increased Efficiency: Industry 4.0 enables manufacturers to optimize their operations quickly and efficiently by knowing what needs attention, which leads to increased efficiency and productivity.
Improved Quality: Industry 4.0 enables manufacturers to detect errors immediately rather than at later stages when repair work is more expensive, which leads to improved quality and reduced waste.
Mass Customization: Industry 4.0 enables manufacturers to produce goods more efficiently and productively across the value chain. Flexibility is improved so manufacturers can better meet customer demands using mass customization.
Improved Supply Chain Management: Industry 4.0 enables manufacturers to schedule deliveries better by sharing production data with suppliers, transforming how manufacturers resource their raw materials and deliver their finished products.
Challenges:

While Industry 4.0 offers several advantages, it also presents several challenges, including:
Cost: Implementing Industry 4.0 technologies can be expensive, and many companies may not have the resources to invest in them.
Skills Gap: Industry 4.0 requires a highly skilled workforce to operate and maintain the new technologies. However, there is a significant skills gap in the manufacturing industry, and many companies may struggle to find the talent they need.
Data Security: Industry 4.0 generates vast amounts of data, which can be a target for cyber-attacks. Companies must ensure that their data is secure and protected from unauthorized access.
In the ecosystem of Industry 4.0, we have considered certain technologies collectively termed as manufacturing using digital technology. Below are the brief details of some of the technology:
Industry 4.0 Market (2021-2026)
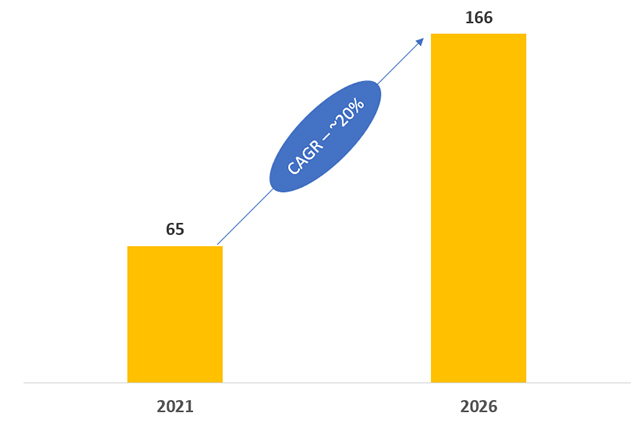
Source – MarketsandMarkets

Industrial robots are essential to Industry 4.0, enabling digital manufacturing. As robots become more intelligent, flexible, and collaborative, they are helping businesses to improve productivity, quality, and efficiency while reducing costs and environmental impact. For example, industrial robots can perform complex and repetitive tasks, such as welding, assembly, and packaging, with greater precision and accuracy than human workers. They are also being used to collect and analyze data from the factory floor, providing insights into production processes that can be used to optimize performance and predict maintenance needs. Additionally, industrial robots are increasingly being used to collaborate with human workers, allowing humans to focus on more complex and value-added tasks. This partnership between humans and robots is essential for realizing the full potential of Industry 4.0. Industrial Robots are expected to grow at a CAGR of ~14% during the forecasted period.

Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize manufacturing in Industry 4.0 by enabling secure, transparent, and efficient transactions and data sharing throughout the supply chain. It can be used to track the provenance of raw materials, ensure the quality of products, streamline payments between manufacturers and suppliers, and create new business models, such as peer-to-peer manufacturing and product-as-a-service.Here are some specific examples of how blockchain is being used in manufacturing today:
- Tracking the provenance of raw materials: Blockchain can create an immutable record of the origin and movement of raw materials from the mine to the factory. This can help ensure ethical sourcing and empower consumers to make informed choices about what they buy.
- Ensuring the quality of products: Blockchain can be used to trace the manufacturing process of products and flag any potential quality issues. This can help to mitigate the risk of defective products reaching consumers.
- Streamlining payments between manufacturers and suppliers: Blockchain can automate payments between manufacturers and suppliers, removing the need for intermediaries and slashing costs.
- Creating new business models: Blockchain can enable new business models, such as peer-to-peer manufacturing and product-as-a-service. Peer-to-peer manufacturing platforms facilitate resource sharing and collaboration among manufacturers, while product-as-a-service models allow customers to pay for product usage rather than outright ownership.
Artificial Intelligence in Manufacturing:

Artificial intelligence (AI) is a critical driver of Industry 4.0, transforming manufacturing by automating tasks, enhancing quality control, and optimizing production processes. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data from sensors and other sources to identify patterns and trends that would be challenging or impossible for humans to detect. This information can then be used to make more informed decisions about production planning, predictive maintenance, and quality control.Artificial Intelligence in manufacturing is expected to grow at a CAGR of ~50% during the forecasted period.
Digital twin technology is a crucial enabler of Industry 4.0 manufacturing. It creates a virtual replica of a physical product, process, or system that can be used to simulate and optimize its performance in real-time. This allows manufacturers to identify and resolve potential issues before they occur, improve efficiency and quality, and reduce costs. For example, a digital twin of a production line can be used to simulate different production scenarios and identify the most efficient way to operate it, reducing waste and improving throughput. A product’s digital twin can be used to test its performance in different environments and identify potential design flaws, improving product quality and reducing the need for costly recalls. Digital twins are expected to grow at a CAGR of ~62% during the forecasted period.

Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) are becoming increasingly essential in Industry 4.0 manufacturing. These self-driving vehicles transport materials, products, and people around factory floors, freeing human workers to focus on more complex tasks. AGVs can be programmed to follow various routes and equipped with sensors to avoid obstacles and navigate safely in crowded environments.This makes them ideal for use in a variety of manufacturing applications, including:
Material handling:
AGVs can transport raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods between workstations and storage areas, reducing manual labor and improving efficiency.
Assembly:
AGVs deliver parts and components to assembly lines and transport finished products to quality control and packaging stations, improving the assembly process’s accuracy and consistency.
Warehousing:
AGVs store and retrieve products in warehouses, reducing fulfillment time and improving customer satisfaction.
Automated Guided Vehicles are expected to grow at a CAGR of ~9% during the forecasted period.
Other technologies contributing to the development of Industry 4.0 in the manufacturing ecosystem include machine condition monitoring, industrial sensors, human-machine interfaces, machine vision, and industrial 3D printing.
Overall, Industry 4.0 is expected to grow at a CAGR of ~20% during the forecasted period.
About MarketsandMarkets :
MarketsandMarkets was founded in 2009 with a simple, yet powerful, idea – every disruption is inherently the source of game-changing business opportunities. At that time, everybody was talking about disruptive trends such as AI, IoT, 3D printing, nanotech, robotics, etc. but nobody was certain about the business opportunities associated with them. Upon sensing this significant white space, MarketsandMarkets started exploring these emerging and fast-growing opportunities and soon realized that it was part of a much bigger game. We figured out that the B2B economy was just beginning to undergo a dramatic transformation, wherein roughly $25 trillion of new revenue sources would emerge by the end of 2030. So, we embarked on a journey to help B2B companies monetize their play in this phenomenon.
During the past 13 years, we got to work with more than 10,000 companies and created $140+ billion of revenue impact for them. Consequently, we too evolved from being a market research publisher to a growth enabling firm. We also moulded our entire corporate culture around “GIVE growth” to promote a growth mindset among our 1500+ people workforce. Earlier this year, we made a formal transformation into one of America’s best management consulting firms as per a survey conducted by Forbes – evidently as the only India origin startup in the list of 200 firms. Even among these 200 peers, we stand apart as a blue-ocean alternative because of our unique intellectual property called Knowledge Store – A primary research driven AI-enabled market intelligence platform meant for growth-minded executives.
MarketsandMarkets can be contacted at:
LinkedIn | Twitter | FaceBook | Blog | Instagram | YouTube | E-mail | Web











